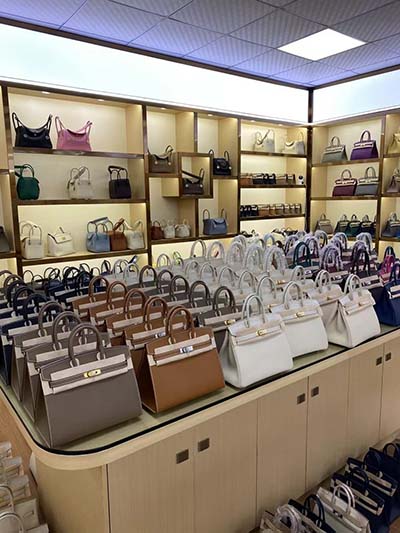
lv non compaction criteria | bi ventricular non compaction cardiomyopathy lv non compaction criteria A maximal endsystolic ratio of NC:C >2 has been established as one of the major criteria to diagnose LVNC by TTE and validated versus anatomical examination of the heart [1]. . Here's an account of my launching of Oystercatcher in July 2015. http://www.ericson25.com/2016/07/oystercatcher-launching-and-renaming.html Roscoe
0 · symptoms of Lv noncompaction
1 · non compaction cardiomyopathy life expectancy
2 · non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines
3 · bi ventricular non compaction cardiomyopathy
4 · Lv non compaction on echo
5 · Lv non compaction guidelines
6 · Lv non compaction echo criteria
7 · Lv non compaction anticoagulation
Mobil Passenger Vehicle Lube, Poland. View Mobil 1™ ESP LV 0W-30. English. Download.
LVNC is characterized by the following features: An altered myocardial wall with prominent trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses, resulting in thickened myocardium . Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted .A maximal endsystolic ratio of NC:C >2 has been established as one of the major criteria to diagnose LVNC by TTE and validated versus anatomical examination of the heart [1]. .
Excessive trabeculation, often referred to as “noncompacted” myocardium, has been described at all ages, from the fetus to the adult. Current evidence for myocardial development, however, . Clinicians and scientists around the globe have advanced our understanding of the genetics, diagnostics, therapeutics, and outcomes for adult and pediatric patients with LVNC. . The objectives of this article are to review the imaging findings of left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) at echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and MDCT; to discuss diagnostic criteria for . American Journal of RoentgenologyLeft ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare congenital phenotype defined by the presence of prominent left ventricular trabeculae, deep intertrabecular recesses (continuous with the .
symptoms of Lv noncompaction
A review of these two criteria suggested that the myocardial thickness is best measured in end-diastole on short-axis images and a non-compacted to compacted ratio >2.0 is diagnostic of . Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and . Criteria for diagnosis by CMR: Petersen et al. (6) described the criteria for the diagnosis by CMR: the ratio of noncompacted myocardium to compacted myocardium must be greater than 2.3 during the diastole (sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 99%).
LVNC is characterized by the following features: An altered myocardial wall with prominent trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses, resulting in thickened myocardium with two layers consisting of noncompacted myocardium and a thin compacted layer of myocardium (picture 1) [6-8]. Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer.
A maximal endsystolic ratio of NC:C >2 has been established as one of the major criteria to diagnose LVNC by TTE and validated versus anatomical examination of the heart [1]. Compared to echocardiography, our CCT NC:C threshold of ≥1.8 NC:C is somewhat lower.Excessive trabeculation, often referred to as “noncompacted” myocardium, has been described at all ages, from the fetus to the adult. Current evidence for myocardial development, however, does not support the formation of compact myocardium from noncompacted myocardium, nor the arrest of this process to result in so-called noncompaction. Clinicians and scientists around the globe have advanced our understanding of the genetics, diagnostics, therapeutics, and outcomes for adult and pediatric patients with LVNC. Yet, there continues to be disagreement about diagnostic criteria, management, and classification of this complex phenotype. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. The objectives of this article are to review the imaging findings of left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) at echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and MDCT; to discuss diagnostic criteria for . American Journal of Roentgenology
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare congenital phenotype defined by the presence of prominent left ventricular trabeculae, deep intertrabecular recesses (continuous with the ventricular cavity), and a thin compacted layer.A review of these two criteria suggested that the myocardial thickness is best measured in end-diastole on short-axis images and a non-compacted to compacted ratio >2.0 is diagnostic of LVNC in accord with CMR measurements [24]. Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick.
Criteria for diagnosis by CMR: Petersen et al. (6) described the criteria for the diagnosis by CMR: the ratio of noncompacted myocardium to compacted myocardium must be greater than 2.3 during the diastole (sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 99%). LVNC is characterized by the following features: An altered myocardial wall with prominent trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses, resulting in thickened myocardium with two layers consisting of noncompacted myocardium and a thin compacted layer of myocardium (picture 1) [6-8]. Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer.
A maximal endsystolic ratio of NC:C >2 has been established as one of the major criteria to diagnose LVNC by TTE and validated versus anatomical examination of the heart [1]. Compared to echocardiography, our CCT NC:C threshold of ≥1.8 NC:C is somewhat lower.Excessive trabeculation, often referred to as “noncompacted” myocardium, has been described at all ages, from the fetus to the adult. Current evidence for myocardial development, however, does not support the formation of compact myocardium from noncompacted myocardium, nor the arrest of this process to result in so-called noncompaction. Clinicians and scientists around the globe have advanced our understanding of the genetics, diagnostics, therapeutics, and outcomes for adult and pediatric patients with LVNC. Yet, there continues to be disagreement about diagnostic criteria, management, and classification of this complex phenotype. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
The objectives of this article are to review the imaging findings of left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) at echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and MDCT; to discuss diagnostic criteria for . American Journal of RoentgenologyLeft ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare congenital phenotype defined by the presence of prominent left ventricular trabeculae, deep intertrabecular recesses (continuous with the ventricular cavity), and a thin compacted layer.A review of these two criteria suggested that the myocardial thickness is best measured in end-diastole on short-axis images and a non-compacted to compacted ratio >2.0 is diagnostic of LVNC in accord with CMR measurements [24].
non compaction cardiomyopathy life expectancy
non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines
sephora dior sets
Daudzslāņu aizsardzība. Ekskluzīvas tehnoloģijas, kas pārsniedz ierasto pretvīrusu robežas. Galalietotāju uzdevumi. Automatizēti procesi un citi drošības pasākumi klienta pusē. Sensoru tīkls. Ar mākoni darbināma draudu izmeklēšana un advancēta draudu novēršana. Mākslīgais intelekts. Padziļināta mācīšanās, mašīnmācīšanās un citas .
lv non compaction criteria|bi ventricular non compaction cardiomyopathy